UNIT I: Introduction to Basic Microprocessors: Historical Background, the Harvard and Princeton architecture, The Microprocessor-Based Personal Computer Systems. The Microprocessor 8085, 8088 basics and comparison (Block & Pin diagram only).
syllabus source:
https://csvtu.ac.in/ew/download/b-tech-5th-semester-5/?wpdmdl=14364&refresh=63c10f5a398271673596762
Prerequisite: Study the following Block diagram first to answer the Questions.
1. Block diagram for the Harvard and Princeton architecture.
2. Block Diagram for Microprocessor 8085
3. Pin Diagram for Microprocessor 8085
4. 8085 vs 8088
Questions: Compiled from previous year CSVTU QPs
1. Write the Difference between Harvard & Princeton Architecture.
👉Note: The Von Neumann (a.k.a. Princeton) architecture.
|
Parameters |
Von Neumann Architecture |
Harvard Architecture |
|
Definition |
The Von Neumann Architecture is an
ancient type of computer architecture that follows the concept of a
stored-program computer. |
Harvard Architecture is a modern
type of computer architecture that follows the concept of the relay-based
model by Harvard Mark I. |
|
Physical Address |
It uses one single physical
address for accessing and storing both data and instructions. |
It uses two separate physical
addresses for storing and accessing both instructions and data. |
|
Buses (Signal Paths) |
One common signal path (bus) helps
in the transfer of both instruction and data. |
It uses separate buses for the
transfer of both data and instructions. |
|
Number of Cycles |
It requires two clock cycles for
executing a single instruction. |
It executes any instruction using
only one single cycle. |
|
Cost |
It is comparatively cheaper in
cost than Harvard Architecture. |
It is comparatively more expensive
than the Von Neumann Architecture. |
|
Access to CPU |
The CPU is not able to read/write
data and access instructions at the same time. |
The CPU can easily read/write data
as well as access the instructions at any given time. |
|
Uses |
This method comes to play in the
case of small computers and personal computers. |
This architecture is best for
signal processing as well as microcontrollers. |
|
Requirement of Hardware |
As compared to Harvard
Architecture, Von Neumann Architecture requires lesser architecture. It is
because it only needs to reach one common memory. |
This one requires more hardware.
It is because it requires separate sets of data as well as address buses for
individual memory. |
|
Requirement of Space |
This architecture basically
requires less space. |
This architecture comparatively
requires more space. |
|
Usage of Space |
This architecture does not waste
any space. It is because the instruction memory can utilize the left space of
the data memory. It can also happen vice-versa. |
This type of architecture can
result in space wastage. It is because the instruction memory cannot utilize
the leftover space in the data memory. It also cannot happen vice-versa. |
|
Execution Speed |
The speed of execution of the Von
Neumann Architecture is comparatively slower. It is because it is not capable
of fetching the instructions and data both at the same time. |
The overall speed of execution of
Harvard Architecture is comparatively faster. It is because the processor, in
this case, is capable of fetching both instructions and data at the very same
time. |
|
Controlling |
The process of controlling becomes
comparatively simpler with this architecture. It is because it fetches either
instructions or data at any given time. |
The process of controlling becomes
comparatively complex with this architecture. It is because it basically
fetches both instructions and data simultaneously at the very same time. |
2. Draw & Explain the Internal Architecture of 8085 in brief.
or
Explain the internal architecture of 8085 microprocessor with basic functional block.
Ans:
3. Give Classification of Pin in 8085 with neat Diagram
Ans: Pin Diagram of 8085:
The pins of a 8085 microprocessor
can be classified into seven groups:
Address bus: A15-A8
Data bus: AD7-AD0, it
carries the least significant 8-bit address and data bus.
Control and status signals: Control signals are RD, WR & ALE, Status
signals are IO/M, S0 & S1
Power supply: VCC &
VSS.
Clock signals: 3 clock signals, i.e. X1, X2, CLK OUT
Interrupts & externally
initiated signals: There are 5 interrupt signals, i.e. TRAP, RST 7.5, RST
6.5, RST 5.5, and INTR.
HOLD , HLDA (HOLD Acknowledge).
Serial I/O signals: SID and
SOD.
4. Give Comparison between Microprocessor 8085 and 8086.
Ans. Also refer the Architecture and pin diagram of 8085 and 8086.
Comparison between 8085 & 8086 Microprocessor
Size − 8085 is 8-bit microprocessor, whereas 8086 is 16-bit microprocessor.
Address Bus − 8085 has 16-bit address bus while 8086 has 20-bit address bus.
Memory − 8085 can access up to 64Kb, whereas 8086 can access up to 1 Mb of memory.
Instruction − 8085 doesn’t have an instruction queue, whereas 8086 has an instruction queue.
Pipelining − 8085 doesn’t support a pipelined architecture while 8086 supports a pipelined architecture.
I/O − 8085 can address 2^8 = 256 I/O's, whereas 8086 can access 2^16 = 65,536 I/O's.
Cost − The cost of 8085 is low whereas that of 8086 is high.
5. Give Pin Diagram of 8086 with neat label of pin Diagram.
o 8086 Microprocessor is an enhanced version of 8085 Microprocessor
Designed by Intel in 1976.It is a 16-bit Microprocessor, 20 address lines 16 data lines, Provides up to 1MB storage. It consists of powerful instruction set, which provides operations like multiplication and division easily.
6. Draw the Internal Architecture of 8086 and Explain the function of each unit of the same in brief.
Ans:
The internal architecture of Intel 8086 is divided into 2 units:
The Bus Interface Unit (BIU), and The Execution Unit (EU).
8086 Architecture
- In order to increase execution speed and fetching speed, 8086 segments the memory.
- Its 20-bit address bus can address 1MB of memory, it segments it into 16 64kB segments.
- 8086 works only with four 64KB segments within the whole 1MB memory.
7. Explain the functions of the following signals of 8085.
(1) ALE
(ii) IO/M
(iii) RD
(iv) READY
(v) TRAP
(vi) INTR & INTA
(vii) HOLD & HLDA
(viii) RESET IN
Ans: Refer pins of 8085
Q. 8085 vs 8086 vs 8088
| 8085 | 8086 | 8088 |
|---|---|---|
| 8085 is an 8 bit microprocessor. | 8086 is a 16 bit microprocessor. | 8088 is a 16 bit microprocessor. |
| It has 8 bit data bus. | 😃It has 16 bit data bus. | 😃It has 8 bit data bus. |
| It has 8 bit ALU. | It has 16 bit ALU. | It has 16 bit ALU. |
| 8085 does not require memory banking as it has an 8 bit data bus. | 8086 requires memory banking to transfer 16 bit data at a time. | 8088 does not require memory banking as it has an 8 bit data bus. |
| 8085 performs slower memory operations as it can transfer only 8 bits in one cycle. | 8086 performs faster memory operations as it can transfer 16 bits in one cycle. | 8088 performs slower memory operations as it can transfer only 8 bits in one cycle. |
| 8085 does not support pipeline architecture. | 8086 supports pipeline architecture. | 8088 supports pipeline architecture. |
| 8085 has no pre-fetch queue as it does not support pipelining. | 8086 has a 6 byte pre-fetch queue for pipelining. | 😃8088 has a 4 byte pre-fetch queue for pipelining. |
| 8085 has an IO/ pin to differentiate between memory and I/O operations. | 8086 has an M/ pin to differentiate between memory and I/O operations. | 8088 has an IO/ pin to differentiate between memory and I/O operations. |
| 8085 has no pre-fetchqueue. | 8086 BIU will fetch new bytes into the pipelining queue when 2 bytes of the queue are empty. | 8088 BIU will fetch a new byte into the pipelining queue when 1 byte of the queue is empty. |
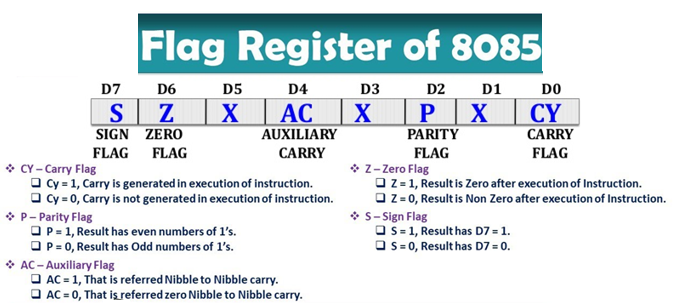
| 8085 has 5 flags. | 8086 has 9 flags. | 8088 has 9 flags. |
😃For further updates do visit this page regularly.
Thank you all
Images may be subject to copyright
~Pradeep Kumar








No comments:
Post a Comment